Copy below to embed:
<a href='https://the-unwinder.com/safety/amazon-supplements-infographic/'><img src='https://the-unwinder.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/03/amazonPNG.png' alt='Unwinding The Online Supplements Business' 540px border='0'/></a>You can also access and download this image from our Google Drive folder. If you do use the image, attribution to the-unwinder.com would be greatly appreciated.
The Unwinder’s mission is to provide readers with trustworthy information about how to safely and effectively maintain a healthy lifestyle. That’s why we not only recommend health products from reputable brands that have good science behind them—like our best collagen powders review—we also publish in-depth explainers about why you should be careful buying certain health products, like our evaluation of the best (and worst) UV light sanitizers that you can buy.
Over the course of running this site, we’ve grown increasingly concerned about supplements on Amazon. This eventually lead us to publish an investigation into multiple 3rd-party Amazon sellers who hide their true identities, sell supplements with misleading labeling, and have a majority of inauthentic (according to Fakespot) reviews on their product pages. This investigation also includes recommendations for how to avoid buying potentially untrustworthy supplements.
As we further explored Amazon’s massive influence on the supplement industry, we realized that the best way to get the word out about the concerns we have might be a visually-engaging infographic that could be easily shared and embedded in people’s websites and social pages.
If you’re a reader who would like to feature this on your own website, or a website you work for, please feel free. Linking back to the-unwinder.com would be greatly appreciated.
Below is the text of the infographic for those who are visually impaired, and for those doing further research on this subject. Please feel free to use anything from the outline in any writing that references this article.
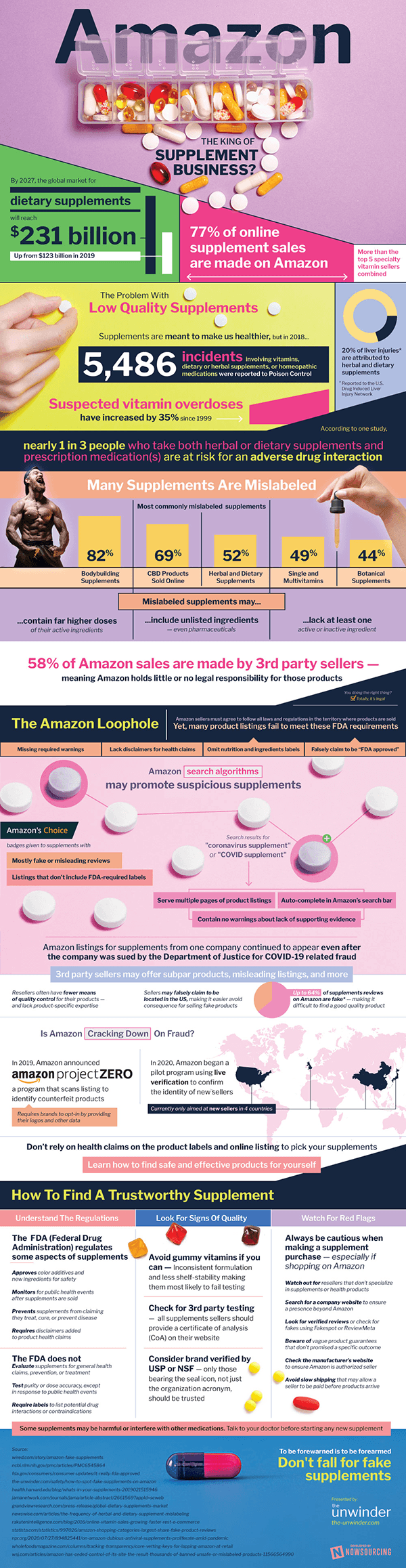
Amazon: King Of The Supplement Business?
By 2027, the global market for dietary supplements will reach $231 billion — Up from $123 billion in 2019.
In 2016, 77% of online supplement sales were made on Amazon — more than any other e-commerce site.
The Problem With Low Quality Supplements
- Supplements are meant to make us healthier, BUT
- In 2018, 5,486 incidents involving vitamins, dietary or herbal supplements, or homeopathic medications were reported to Poison Control
- Suspected vitamin overdoses have increased by 35% since 1999
- 20% of liver injuries* are attributed to herbal and dietary supplements
- According to one study, nearly 1 in 3 people who take both herbal or dietary supplements and prescription medication(s) are at risk for an adverse drug interaction
- In 2018, 5,486 incidents involving vitamins, dietary or herbal supplements, or homeopathic medications were reported to Poison Control
- Many Supplements Are Mislabeled
- 82% of supplements used for bodybuilding
- 69% of CBD products sold online
- 52% of herbal and dietary supplements
- 49% of single and multivitamins
- 44% of botanical supplements
- Mislabeled supplements may
- Contain far higher doses of their active ingredients
- Include unlisted ingredients — even pharmaceuticals
- Lack at least one active or inactive ingredient
58% of Amazon sales are made by 3rd party sellers — meaning Amazon holds little or no legal responsibility for those products.
The Amazon Loophole
- Amazon sellers must agree to follow all laws and regulations in the territory where products are sold — yet, many product listings fail to meet these FDA requirements
- Missing required warnings
- Lack disclaimers for health claims
- Omit nutrition and ingredients labels
- Falsely claim to be “FDA approved”
- Amazon search algorithms may promote suspicious supplements
- ”Amazon’s Choice” badges given to supplements with:
- Mostly fake or misleading reviews
- Listings that don’t include FDA-required labels
- Search results for “coronavirus supplement” or “COVID supplement”:
- Auto-complete in Amazon’s search bar
- Serve multiple pages of product listings
- Contain no warnings about lack of supporting evidence
- Amazon listings for supplements from My Doctor Suggests continued to appear even after the company was sued by the Department of Justice for COVID-19 related fraud
- ”Amazon’s Choice” badges given to supplements with:
- 3rd party sellers may offer subpar products, misleading listings, and more
- Resellers often have fewer means of quality control for their products — and lack product-specific expertise
- Sellers may falsely claim to be located in the US, making it easier avoid consequence for selling fake products
- Up to 64% of supplements reviews on Amazon are considered inauthentic or misleading, according to Fakespot — making it difficult to find a good quality product
- Is Amazon Cracking Down On Fraud?
- In 2019, Amazon announced Project Zero, a program that scans listings to identify counterfeit products
- Requires brands to opt-in by providing their logos and other data
- In 2020, Amazon began a pilot program using live verification to confirm the identity of new sellers
- Currently only aimed at new sellers in 4 countries
- In 2019, Amazon announced Project Zero, a program that scans listings to identify counterfeit products
Don’t rely on health claims on the product labels and online listing to pick your supplements — learn how to find safe and effective products for yourself.
How To Find A Trustworthy Supplement
- Understand The Regulations
- The Federal Drug Administration (FDA) regulates some aspects of supplements
- Approves color additives and new ingredients for safety
- Monitors for public health events after supplements are sold
- Prevents supplements from claiming they treat, cure, or prevent disease
- Requires disclaimers added to product health claims
- The FDA does not
- Evaluate supplements for general health claims, prevention, or treatment
- Test purity or dose accuracy, except in response to public health events
- Require labels to list potential drug interactions or contraindications
- The Federal Drug Administration (FDA) regulates some aspects of supplements
- Look For Signs Of Quality
- Avoid gummy vitamins if you can — inconsistent formulation and less shelf-stability making them most likely to fail testing
- Check for 3rd party testing — all supplements sellers should provide a certificate of analysis (CoA) on their website
- Consider brand verified by USP or NSF — only those bearing the seal icon, not just the organization acronym, should be trusted
- Watch For Red Flags
- Watch out for resellers that don’t specialize in supplements or health products
- Search for a company website to ensure a presence beyond Amazon
- Look for verified reviews or check for fakes using Fakespot or ReviewMeta
- Beware of vague product guarantees that don’t promised a specific outcome
- Check the manufacturer’s website to ensure Amazon is authorized seller
- Avoid slow shipping that may allow a seller to be paid before products arrive
Always be cautious when making a supplement purchase — especially if shopping on Amazon.
Some supplements may be harmful or interfere with other medications. Talk to your doctor before starting any new supplement.
*Reported to the U.S. Drug Induced Liver Injury Network
Sources
- https://www.grandviewresearch.com/press-release/global-dietary-supplements-market
- https://www.rakutenintelligence.com/blog/2016/online-vitamin-sales-growing-faster-rest-e-commerce
- https://www.newswise.com/articles/the-frequency-of-herbal-and-dietary-supplement-mislabeling
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6545864/
- https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/article-abstract/2661569?appId=scweb
- https://www.fda.gov/consumers/consumer-updates/it-really-fda-approved
- https://www.health.harvard.edu/blog/whats-in-your-supplements-2019021515946
- https://www.wired.com/story/amazon-fake-supplements/
- https://wholefoodsmagazine.com/columns/tracking-transparency/core-vetting-keys-for-lapping-amazon-at-retail/
- https://www.wsj.com/articles/amazon-has-ceded-control-of-its-site-the-result-thousands-of-banned-unsafe-or-mislabeled-products-11566564990
- https://the-unwinder.com/safety/how-to-spot-fake-supplements-on-amazon/
- https://www.npr.org/2020/07/27/894825441/on-amazon-dubious-antiviral-supplements-proliferate-amid-pandemic
- https://www.statista.com/statistics/997026/amazon-shopping-categories-largest-share-fake-product-reviews/
- https://piper.filecamp.com/uniq/meDKF2EpE2jsmTOs.pdfhttps://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6145997/
- https://www.forbes.com/sites/wadeshepard/2017/01/02/amazon-scams-on-the-rise-in-2017-as-fraudulent-sellers-run-amok-and-profit-big/#153dfe203ea6
- https://techcrunch.com/2019/02/28/amazon-launches-new-tools-that-allow-brands-to-proactively-fight-counterfeiting/
- https://www.theverge.com/2020/4/27/21238026/amazon-seller-verification-video-calling-fraud-third-party-sellers